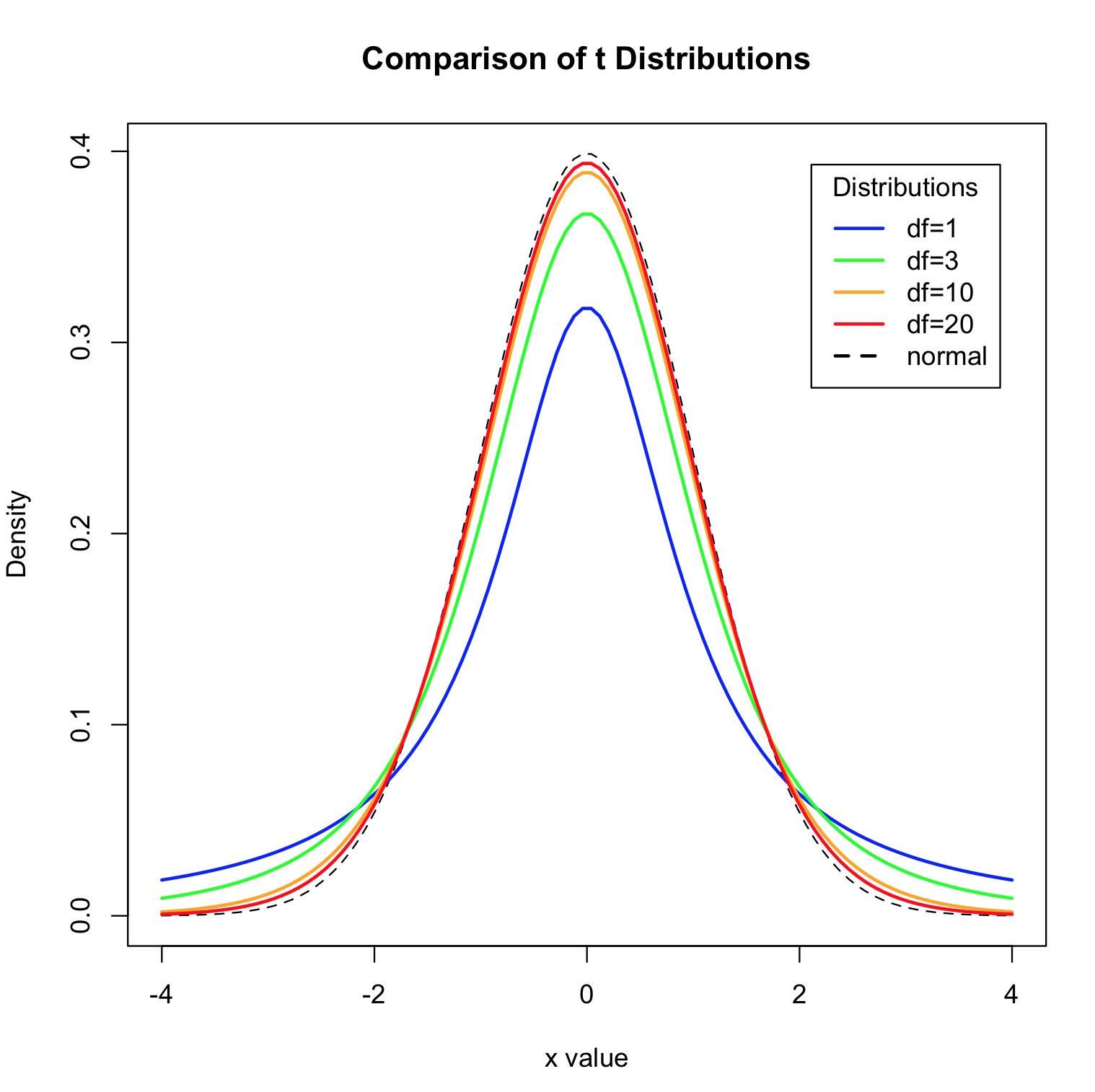
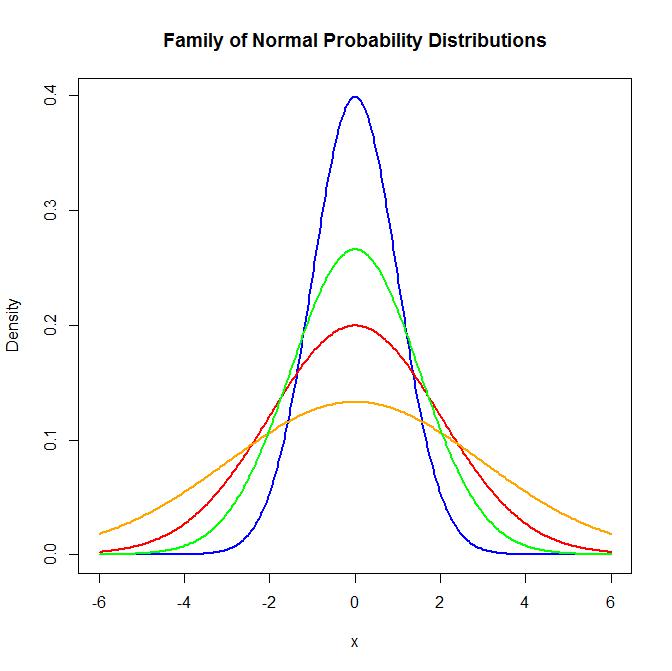
A discrete variable cannot take the value of a fraction between one value and. Age height score on an exam response on a likert scale on a survey are all continuous variable.

Discrete Vs Continuous Data Definition Examples And Difference
Examples of continuous variables are height and weight. Examples of continuous variables are height and weight. They can assume a finite number of isolated values. So it is continuous variation. What are some examples of continuous normal random variables. The other possible type of variable is called a discrete variable. Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups.
This includes rankings eg. Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts eg. Height weight or age. Biometric measures such as height weight blood pressure etc rainfall amounts in an area. Examples of continuous variables include height time age and temperature. It can be ordinal interval or ratio types.
Finishing places in a race classifications eg. Rank ordering data simply puts the data on an ordinal scale. A continuous variable is any variable that can be any value in a certain range. For example between 50 and 72 inches there are literally millions of possible heights. For a pair of variables r squared is simply the square of the pearsons correlation coefficient. For any species a characteristic that changes gradually over a range of values shows continuous variation.
For example squaring the height weight correlation coefficient of 0694 produces an r squared of 0482 or 482. In other words height explains about half the variability of weight in preteen girls. On the other hand continuous variables are variables for which the values are not countable and have an infinite number of possibilitiesfor example. Brands of cereal and binary outcomes eg. The continuous variables can take any value between two numbers. 5204762 inches 69948376 inches and etc.
Nyc media labcc by sa 20 some examples of continuous variables are measuring peoples weight within a certain range measuring the amount of gas put into a gas tank or measuring the height of people. Examples of continuous variables are blood pressure height weight income and age. For simplicity we usually referred to years kilograms or pounds and centimeters or feet and inches for age weight and height respectively. A discrete variable is a numeric variable which can take a value based on a count from a set of distinct whole values. True the closer the points lie on a scatter plot with respect to the straight line of best fit through them the stronger the association between the variables. The normal distribution can.
Test scores of a large sample tax revenue generated across states etc. Examples of such characteristics are.