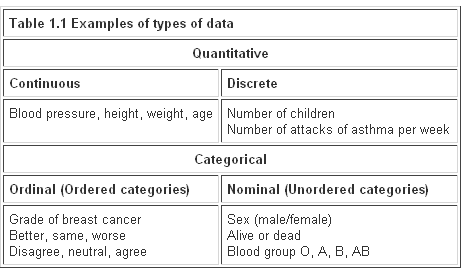
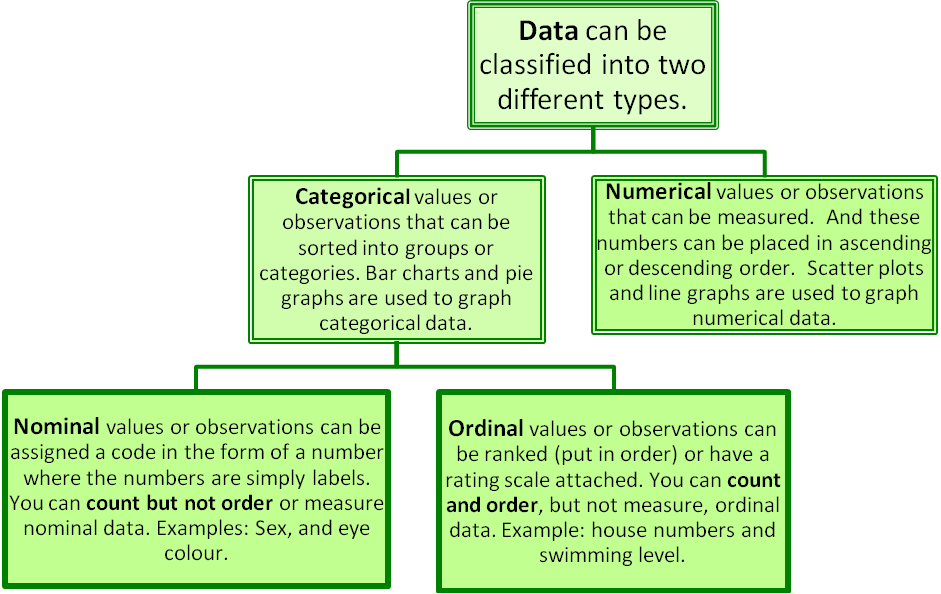
Nominal ordinal interval and ratiothese were developed by psychologist stanley smith stevens who wrote about them in a 1946 article in science titled on the theory of scales of measurementeach level of measurement and its corresponding scale is able to measure one or more of the four properties of. Common examples would be gender eye color or ethnicity.
Types Of Data Amp The Scales Of Measurement Unsw Online
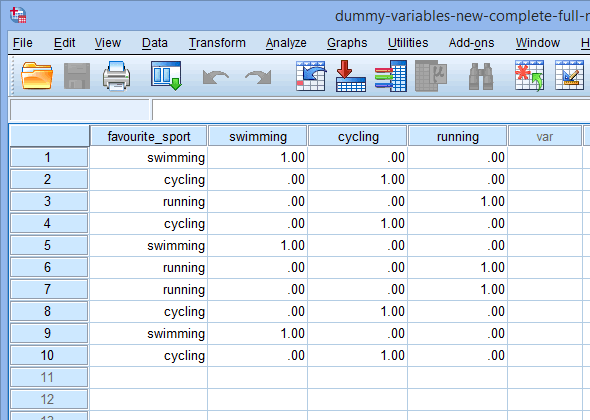
Height and weight ordinal nominal. First second third and so on. The ordinal level of measurement is a more sophisticated scale than the nominal level. A scale used to label variables that have no quantitative values. Your height and weight are examples of which level of measurement. Ratio true for this case we have a clear definition of the 0 since the 0 for the heigth and the weigth represent absence of mass. Knowing the scale of measurement for a variable is an important aspect in choosing the right statistical analysis.
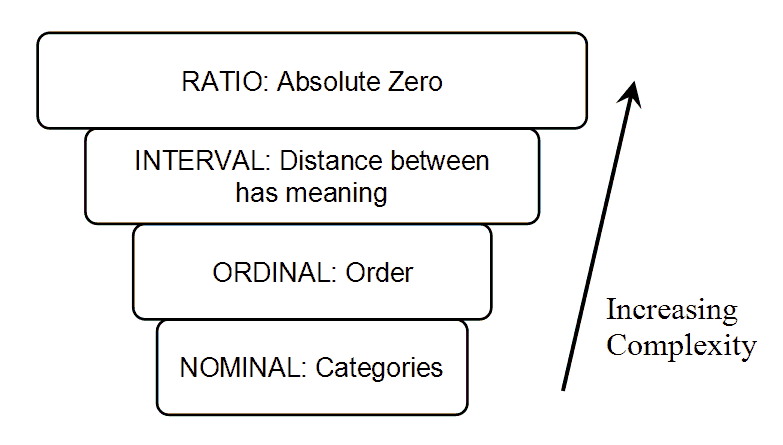
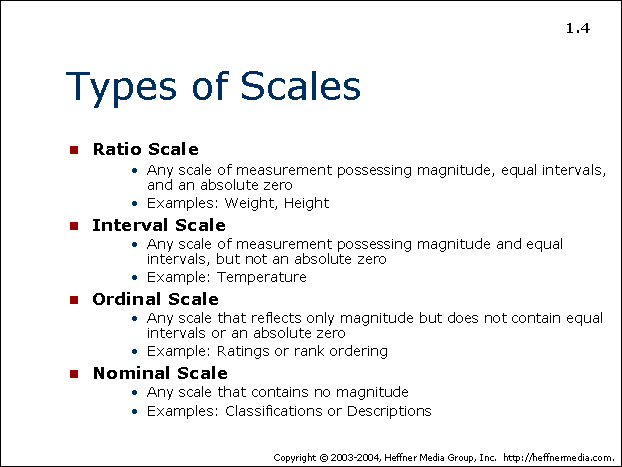
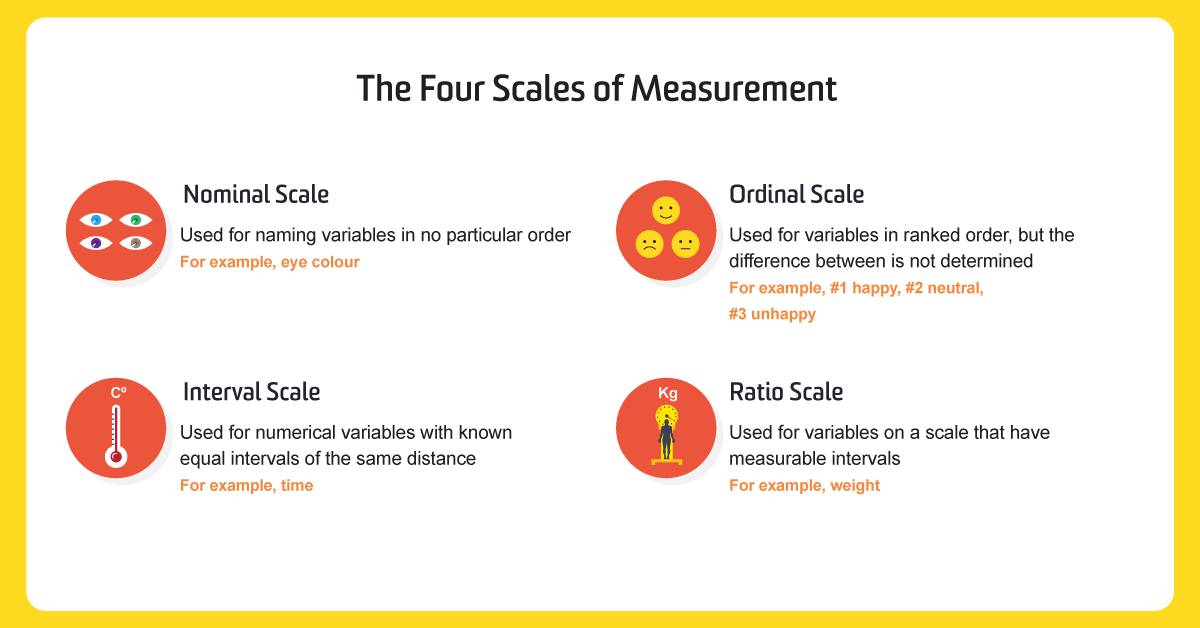
In the 1940s stanley smith stevens introduced four scales of measurement. Each level of measurement has some important properties that are useful to know. Within science there are four commonly used levels and scales of measurement. However ordinal variables are still categorical and do not provide precise measurements. Examples of continuous variables include height time age and temperature. With the option of true zero varied inferential and descriptive analysis techniques can be applied to the variables.
These are still widely used today as a way to describe the characteristics of a variable. The simplest measurement scale we can use to label variables is a nominal scale. In summary nominal variables are used to name or label a series of valuesordinal scales provide good information about the order of choices such as in a customer satisfaction surveyinterval scales give us the order of values the ability to quantify the difference between each onefinally ratio scales give us the ultimateorder interval values plus the ability to calculate. Weight in kilograms is a very good example since it has a definite ratio from one weight to another. Nominal when there is no natural ordering among the categories. In addition to the fact that the ratio scale does everything that a nominal ordinal and interval scale can do it can also establish the value of absolute zero.
Ordinal numbers denote an items position or rank in a sequence. Classify each of the following as nominal ordinal interval or ratio data. 50kg is indeed twice as heavy as 25 kg. Ordinal when there is a natural order among the categories such as ranking scales or letter grades. Nominal ordinal interval or ratio. Nominal ordinal interval and ratio.
Profitloss in dollars a companys tax identification number outside temperature in celcius. In this post we define each measurement scale and provide examples of variables that can be used with each scale. This scale enables us to order the items of interest using ordinal numbers. The best examples of ratio scales are weight and height. False by definition and ordinal variable is which one that cant be represented by numeric values and for this case the weight and the height are not example of this definition. The trade balance in dollars.