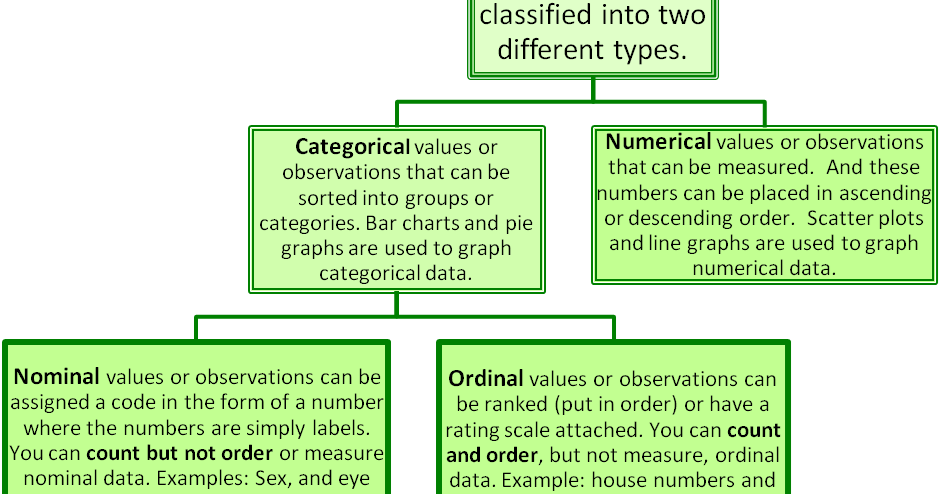
A person who is 12 metres 4 feet tall is two thirds as tall as a 18 metre 6 foot tall person. Levels and scales of measurement are corresponding ways of measuring and organizing variables when conducting statistical research.

Interval Scale Vs Ratio Scale What Is The Difference
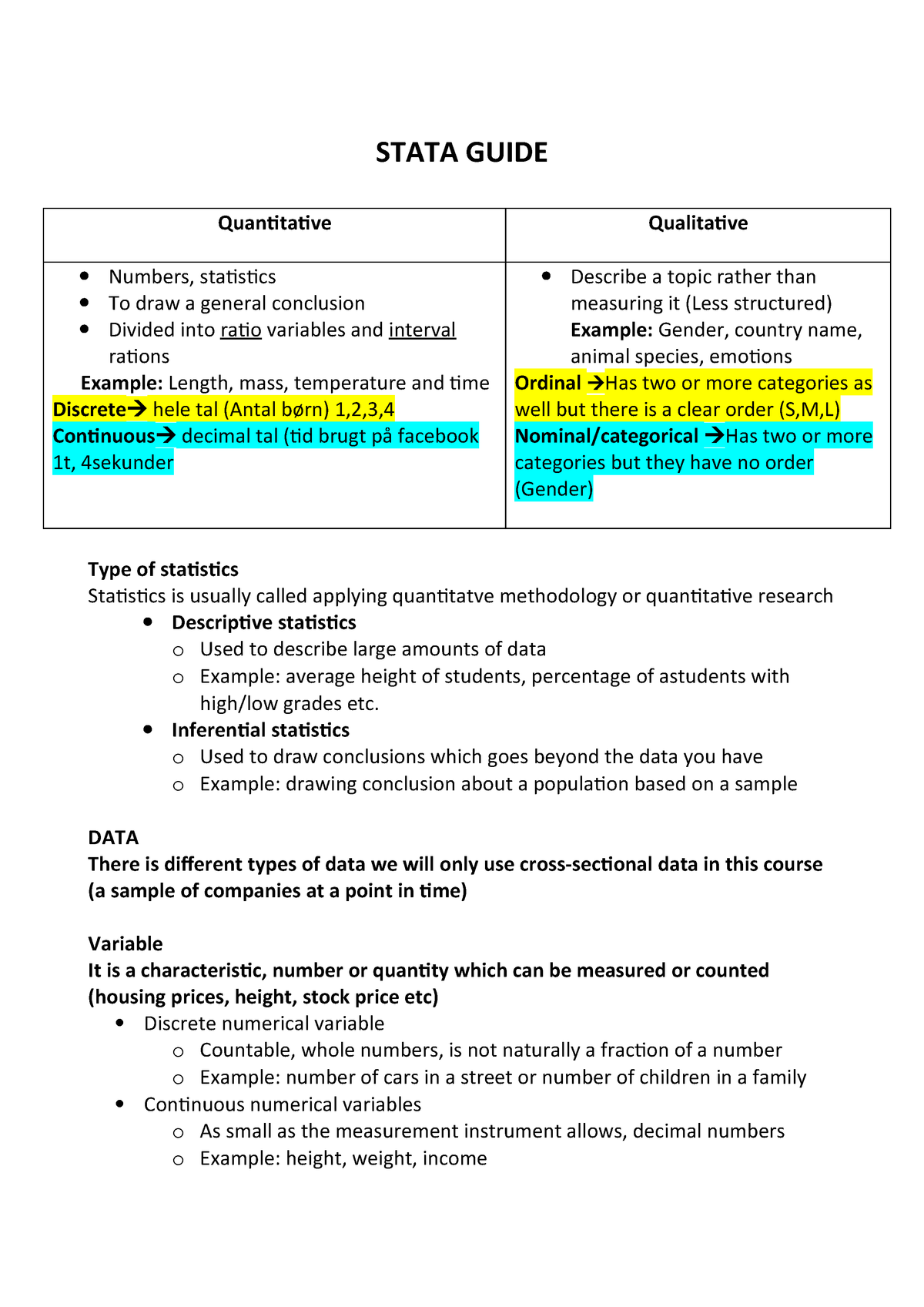
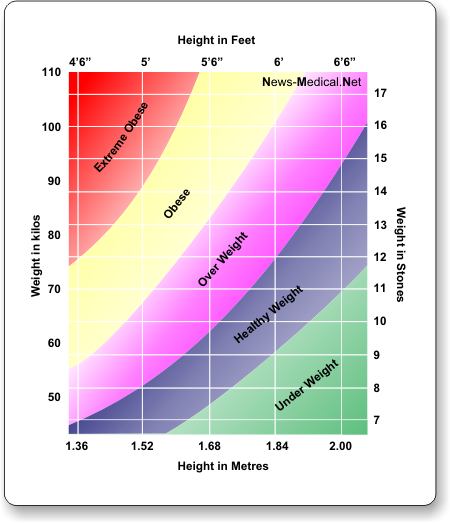
Measuring height and weight are examples of which type of research. The units are divided into kilograms and grams. Physical characteristics of persons and objects can be measured with ratio scales and thus height and weight are examples of ratio measurement. Many statistical methods are appropriate only for data of certain measurement scales. An example of the ratio level of measurement is weight. The scale on the left can measure weight between text0 and text2 textkg in weight. We can calculate ratios like these because the scale for weight in pounds starts at zero pounds.
Ratios of observations compared with reference values eg. Scales for measuring larger quantities of food like vegetables or fruit are sometimes seen in shops or at markets. Measurement of physical dimensions such as height weight distance age years of experience etc. Are the examples of ratio scale. A person who weights 150 pounds weights twice as much as a person who weighs only 75 pounds and half as much as a person who weighs 300 pounds. Height relative to the mean of a reference population for a given sex and age are difficult to handle as values may fall either side of 1 100.
A score of 0 means there is complete absence of height or weight.